We at Preeti Kidney Hospitals, are committed to providing expert care and innovative treatment options for individuals diagnosed with kidney cancer.
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, originates in the kidneys—two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the ribcage. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste from the blood and producing urine. The most common type of kidney cancer in adults is renal cell carcinoma, which begins in the lining of the small tubes in the kidney. Other less common types include transitional cell carcinoma and Wilms' tumor, the latter primarily affecting children.
While the exact cause of kidney cancer is not always clear, several factors may increase the risk of developing this disease:
Kidney cancer often does not cause symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
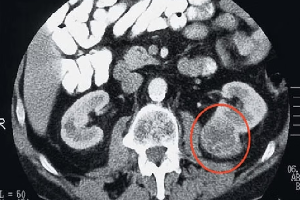
To diagnose kidney cancer, the doctor may recommend several tests:
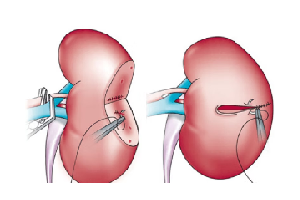
Partial nephrectomy is used to treat kidney cancer that has not spread to other tissue. The aim is to remove the part of the kidney with abnormally growing cells (tumour) but to leave as much as possible of the healthy kidney.
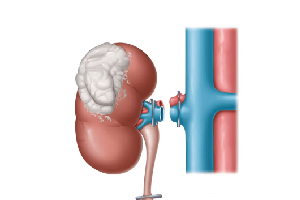
Radical Nephrectomy is where a surgeon removes the entire kidney. Surgeons may also remove a section of the ureter (tube leading to the bladder), in a procedure called nephroureterectomy. They may also remove the adrenal glands (hormone glands that sit above the kidneys). This may also be performed as an open or laparoscopic/robotic procedure.
While it’s not always possible to prevent kidney cancer, certain lifestyle changes can reduce your risk: